Blar i forfatter "Ahmad, Azeem"
-
Automated tilt compensation in acoustic microscopy
Gupta, Shubham Kumar; Habib, Anowarul; Kumar, Prakhar; Melandsø, Frank; Ahmad, Azeem (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-09-12)Scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM) is a potent and nondestructive technique capable of producing three-dimensional topographic and tomographic images of specimens. This is achieved by measuring the differences in time of flight (ToF) of acoustic signals emitted from various regions of the sample. The measurement accuracy of SAM strongly depends on the ToF measurement, which is affected by tilt in ... -
Automatic fringe pattern enhancement using truly adaptive period-guided bidimensional empirical mode decomposition
Gocłowski, Paweł; Trusiak, Maciej; Ahmad, Azeem; Styk, Adam; Mico, Vicente; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Patorski, Krzysztof (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-02-19)Fringe patterns encode the information about the result of a measurement performed via widely used optical full-field testing methods, e.g., interferometry, digital holographic microscopy, moiré techniques, structured illumination etc. Affected by the optical setup, changing environment and the sample itself fringe patterns are often corrupted with substantial noise, strong and uneven background ... -
Characterization of color cross-talk of CCD detectors and its influence in multispectral quantitative phase imaging
Ahmad, Azeem; Kumar, Anand; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Butola, Ankit; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Mehta, Dalip Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2019-02-08)Multi-spectral quantitative phase imaging (QPI) is an emerging imaging modality for wavelength dependent studies of several biological and industrial specimens. Simultaneous multi-spectral QPI is generally performed with color CCD cameras. Here, we present a new approach for accurately measuring the color crosstalk of 2D area detectors, without needing prior information about camera specifications. ... -
Characterization of Liposomes Using Quantitative Phase Microscopy (QPM)
Cauzzo, Jennifer; Jayakumar, Nikhil; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Ahmad, Azeem; Skalko-Basnet, Natasa (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-04-21)The rapid development of nanomedicine and drug delivery systems calls for new and effective characterization techniques that can accurately characterize both the properties and the behavior of nanosystems. Standard methods such as dynamic light scattering (DLS) and fluorescent-based assays present challenges in terms of system’s instability, machine sensitivity, and loss of tracking ability, among ... -
Chip-based multimodal super-resolution microscopy for histological investigations of cryopreserved tissue sections
Villegas, Luis; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Nystad, Mona; Tinguely, Jean-Claude; Coucheron, David Andre; Dullo, Firehun Tsige; Priyadarshi, Anish; Acuna Maldonado, Sebastian Andres; Ahmad, Azeem; Mateos, Jose M.; Barmettler, Gery; Ziegler, Urs; Birgisdottir, Åsa Birna; Hovd, Aud-Malin Karlsson; Fenton, Kristin Andreassen; Acharya, Ganesh; Agarwal, Krishna; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-02-24)Histology involves the observation of structural features in tissues using a microscope. While diffraction-limited optical microscopes are commonly used in histological investigations, their resolving capabilities are insufficient to visualize details at subcellular level. Although a novel set of super-resolution optical microscopy techniques can fulfill the resolution demands in such cases, the ... -
Deep learning architecture “LightOCT” for diagnostic decision support using optical coherence tomography images of biological samples
Butola, Ankit; Prasad, Dilip Kumar; Ahmad, Azeem; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Qaiser, Darakhshan; Srivastava, Anurag; Senthilkumaran, Paramasivam; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Mehta, Dalip Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-08-13)Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is being increasingly adopted as a label-free and non-invasive technique for biomedical applications such as cancer and ocular disease diagnosis. Diagnostic information for these tissues is manifest in textural and geometric features of the OCT images, which are used by human expertise to interpret and triage. However, it suffers delays due to the long process of ... -
Demystifying speckle field interference microscopy
Ahmad, Azeem; Jayakumar, Nikhil; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-06-27)Dynamic speckle illumination (DSI) has recently attracted strong attention in the feld of biomedical imaging as it pushes the limits of interference microscopy (IM) in terms of phase sensitivity, and spatial and temporal resolution compared to conventional light source illumination. To date, despite conspicuous advantages, it has not been extensively implemented in the feld of phase imaging due ... -
Effect on the longitudinal coherence properties of a pseudothermal light source as a function of source size and temporal coherence
Ahmad, Azeem; Mahanty, Tanmoy; Dubey, Vishesh; Butola, Ankit; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Mehta, Dalip Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2019-04-01)In the present Letter, a synthesized pseudothermal light source having high temporal coherence (TC) and low spatial coherence (SC) properties is used. The longitudinal coherence (LC) properties of the spatially extended monochromatic light source are systematically studied. The pseudothermal light source is generated from two different monochromatic laser sources: He–Ne (at 632 nm) and DPSS (at 532 ... -
Finite element simulation of transmission and reflection of acoustic waves in the ultrasonic transducer
Shukla, Kaushik; Ahmad, Azeem; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Melandsø, Frank; Habib, Anowarul (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-03-30)In scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM), the image quality depends on several factors such as noise level, resolution, and interaction of the waves with sample boundaries. The theoretical equations for the reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient are suitable for plane boundaries but fail for curved/rough boundaries. We presented a finite element method-based modeling for the loss ... -
Finite element simulation of transmission and reflection of acoustic waves in the ultrasonic transducer
Shukla, Kaushik; Ahmad, Azeem; Habib, Anowarul; Singh Ahluwalia, Balpreet; Melandsø, Frank (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2022-03-30)In scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM), the image quality depends on several factors such as noise level, resolution, and interaction of the waves with sample boundaries. The theoretical equations for the reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient are suitable for plane boundaries but fail for curved/rough boundaries. We presented a finite element method-based modeling for the loss ... -
High space-bandwidth in quantitative phase imaging using partially spatially coherent digital holographic microscopy and a deep neural network
Butola, Ankit; Kanade, Sheetal Raosaheb; Bhatt, Sunil; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Kumar, Anand; Ahmad, Azeem; Prasad, Dilip K.; Senthilkumaran, Paramasivam; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Mehta, Dalip Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-11-16)Quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) is a label-free technique that enables monitoring of morphological changes at the subcellular level. The performance of the QPM system in terms of spatial sensitivity and resolution depends on the coherence properties of the light source and the numerical aperture (NA) of objective lenses. Here, we propose high space-bandwidth quantitative phase imaging using ... -
High spatially sensitive quantitative phase imaging assisted with deep neural network for classification of human spermatozoa under stressed condition
Butola, Ankit; Popova, Daria; Prasad, Dilip K.; Ahmad, Azeem; Habib, Anowarul; Tinguely, Jean-Claude; Basnet, Purusotam; Acharya, Ganesh; Paramasivam, Senthilkumaran; Mehta, Dalip Singh; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-08-04)Sperm cell motility and morphology observed under the bright field microscopy are the only criteria for selecting a particular sperm cell during Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) procedure of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). Several factors such as oxidative stress, cryopreservation, heat, smoking and alcohol consumption, are negatively associated with the quality of sperm cell and ... -
High-throughput spatial sensitive quantitative phase microscopy using low spatial and high temporal coherent illumination
Ahmad, Azeem; Dubey, Vishesh; Jayakumar, Nikhil; Habib, Anowarul; Butola, Ankit; Nystad, Mona; Acharya, Ganesh; Basnet, Purusotam; Mehta, Dalip Singh; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2021-08-04)High space-bandwidth product with high spatial phase sensitivity is indispensable for a single-shot quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) system. It opens avenue for widespread applications of QPM in the field of biomedical imaging. Temporally low coherence light sources are implemented to achieve high spatial phase sensitivity in QPM at the cost of either reduced temporal resolution or smaller field ... -
Highly sensitive quantitative phase microscopy and deep learning aided with whole genome sequencing for rapid detection of infection and antimicrobial resistance
Ahmad, Azeem; Hettiarachchi, Ramith; Khezri, Abdolrahman; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Wadduwage, Dushan; Ahmad, Rafi (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-04-12)Current state-of-the-art infection and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) diagnostics are based on culture-based methods with a detection time of 48–96 h. Therefore, it is essential to develop novel methods that can do real-time diagnoses. Here, we demonstrate that the complimentary use of label-free optical assay with whole-genome sequencing (WGS) can enable rapid diagnosis of infection and AMR. Our ... -
Highly temporal stable, wavelength-independent, and scalable field-of-view common-path quantitative phase microscope
Ahmad, Azeem; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Butola, Ankit; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Mehta, Dalip Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2020-11-11)<p><i>Significance:</i> High temporal stability, wavelength independency, and scalable field of view (FOV) are the primary requirements of a quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) system. The high temporal stability of the system provides accurate measurement of minute membrane fluctuations of the biological cells that can be an indicator of disease diagnosis. <p><i>Aim:</i> The main aim of this work ... -
Image denoising in acoustic microscopy using block-matching and 4D filter
Gupta, Shubham Kumar; Pal, Rishant; Ahmad, Azeem; Melandsø, Frank; Habib, Anowarul (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-08-14)Scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM) is a label-free imaging technique used in biomedical imaging, non-destructive testing, and material research to visualize surface and sub-surface structures. In ultrasonic imaging, noises in images can reduce contrast, edge and texture details, and resolution, negatively impacting post-processing algorithms. To reduce the noises in the scanned image, we have employed ... -
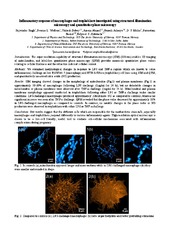
Inflammatory response of macrophages and trophoblasts investigated using structured illumination microscopy and quantitative phase microscopy
Singh, Rajwinder; Wolfson, Deanna Lynn; Dubey, Vishesh; Ahmad, Azeem; Acharya, Ganesh; Mehta, Dalip Singh; Basnet, Purusotam; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-09)<i>Introduction</i>: The super-resolution capability of structured illumination microscopy (SIM) (100 nm) enables 3D imaging of mitochondria, and label-free quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) provides nanoscale quantitative phase values relating to cellular thickness and the refractive index of cellular content. -
Label-free imaging on waveguide platform with enhanced resolution and contrast
Jayakumar, Nikhil; Dullo, Firehun Tsige; Dubey, Vishesh Kumar; Ahmad, Azeem; Cauzzo, Jennifer; Mazagao Guerreiro, Eduarda; Snir, Omri; Skalko-Basnet, Natasa; Agarwal, Krishna; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Conference object; Konferansebidrag, 2021)Chip-based Evanescent Light Scattering (cELS) utilizes the multiple modes of a high-index contrast optical waveguide for near-field illumination of unlabeled samples, thereby repositioning the highest spatial frequencies of the sample into the far-field. The multiple modes scattering off the sample with different phase differences is engineered to have random spatial distributions within the integration ... -
Laser-Generated Scholte Waves in Floating Microparticles
Ranjan, Abhishek; Ahmad, Azeem; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh; Melandsø, Frank (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2023-02-04)This study aims to demonstrate the generation and detection of Scholte waves inside polystyrene microparticles. This was proven using both experimental analysis and COMSOL simulation. Microspheres of different sizes were excited optically with a pulsed laser (532 nm), and the acoustic signals were detected using a transducer (40 MHz). On analyzing the laser-generated ultrasound signals, the results ... -
Multi-modal chip-based fluorescence and quantitative phase microscopy for studying inflammation in macrophages
Dubey, Vishesh; Ahmad, Azeem; Singh, Rajwinder; Wolfson, Deanna; Basnet, Purusotam; Acharya, Ganesh; Mehta, Dalip Singh; Ahluwalia, Balpreet Singh (Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-07-24)Total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy benefits from high-sensitivity, low background noise, low photo-toxicity and high-contrast imaging of sub-cellular structures close to the membrane surface. Although, TIRF microscopy provides high-contrast imaging it does not provide quantitative information about morphological features of the biological cells. Here, we propose an integrated ...


 English
English norsk
norsk